Therapeutic efficacy and prognosis of lung cancer have
been significantly improved owning to the introduction of small molecule
targeted drugs represented by epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors. Mutations
in the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2, ERBB2) have been
identified as oncogenic drivers and occur as high as 6.7% in EGFR/ALK/ROS1
triple-negative non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Historically, patients with
HER2-mutant NSCLC have a median overall survival (OS) of less than 2 years from
the time of stage IV diagnosis. Several patient reports and series reporting on
HER2-targeted agents in patients with HER2-mutant NSCLC have shown limited
clinical activity. Thus, chemotherapy remains the main strategy for these
patients. Therefore, there is an urgent need for effective HER2-targeted drugs
to improve the long-term outcome in this subset of patients.
Pyrotinib (developed by Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine) is
an oral, irreversible pan-HER receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) with
activity against epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/HER1 and HER2. Giving its
excellent performance in preclinical and 1-2 clinical studies, it has been
approved for the treatment of breast cancer. Prof. Zhou Caicun and Prof. Ren
Shengxiang (Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine)
with Prof Ji Hongbin (Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai
Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences) utilized a
patient-derived organoid with HER2-A775_G776YVMA-inserted advanced lung
adenocarcinoma and HER2 exon 20 insertion patient-derived xenografts (PDX)
model to test the antitumor effect of pyrotinib in the preclinical setting. The
results of the study were published in the latest issue of the EUROPEAN SOCIETY
FOR MEDICAL ONCOLOGY (ESMO) official journal "Annals of Oncology" (2017
impact factor: 13.930). The paper also presented results of clinical studies,
first reported the efficacy and safety of Pyrotinib in the treatment of HER2
mutant non-small cell lung cancer.
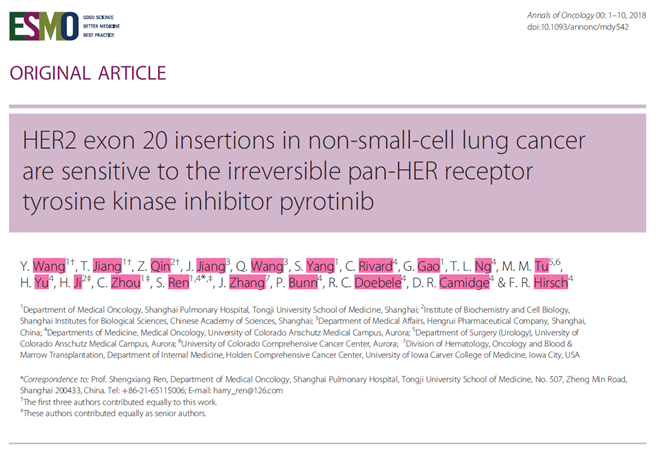
The results are as follows:
Generation of a HER2-20 exon A775_G776YVMA insertion
mutant patient-derived lung adenocarcinoma organoid model.
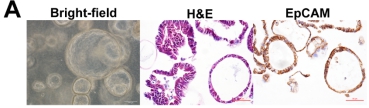
Pyrotinib showed superior anti-tumor activity in
animal experiments over other drugs.
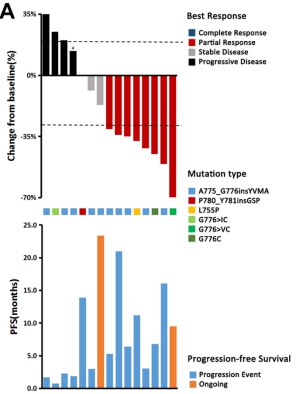
They provided clinical evidence of the activity of
pyrotinib in 15 patients with HER2-mutant NSCLC with an ORR of 53.3% and a
median PFS of 6.4 months in our phase II study. PFS of 4 patients exceeded 1
year and 1 patient exceeded 2 years. Among them, 67% (10/15) of the patients
were confirmed to have A775_G776YVMA insertion mutation, Pyrotinib also
effective against other HER2 mutation types such as G776C, G776>VC, L755P,
and P780_Y781insGSP.
This study revealed Pyrotinib has a significant effect
on HER2 mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Based on this, researchers initiated
a multi-center phase II trial (NCT02834936) afterwards, currently completed and
the final results will be announced soon. The drug is expected to bring more
survival benefits to patients with advanced lung cancer with HER2 mutation. In
addition, organoid model could be used well as a tool for drug-induced
mutations precise treatment, especially for rare mutations, its application
prospects are broad.
Prof. Zhou Caicun (Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital
affiliated to Tongji University), Prof. Ren Shengxiang (Shanghai Pulmonary
Hospital affiliated to Tongji University) and Prof. Ji Hongbin (Institute of
Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences,
Chinese Academy of Sciences) are corresponding authors; Dr. Wang Yan (Shanghai
Pulmonary Hospital affiliated to Tongji University), Dr. Jiang Tao (Shanghai
Pulmonary Hospital affiliated to Tongji University) and Dr. Qin Zhen (Institute
of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences,
Chinese Academy of Sciences) are co-first authors. Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine
provided important support for the research. In addition, this study was
supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the ‘Shuguang
Program’, Science and Technology Commission of
Shanghai Municipality, and the Development Fund for Shanghai Talents.
