The production of widely
different and specialized cell types from a single omnipotent zygote involves
large-scale transcriptional changes and chromatin recombination. Pioneer
transcription factors play a key role in the programming of the epigenome and are
capable to facilitate the recruitment of other regulatory factors in the standardization and
differentiation steps of the continuous cell lineage. Research group of Prof.
Liang Xingqun and Sun Yunfu published a research paper entitled as Pioneering
function of Isl1 in the epigenetic control of cardiomyocyte fate on
Cell Research online. The study revealed that the Isl1 / Brg1-Baf60c
complex plays a crucial role in coordinating cardiac development and
establishing epigenetic memory of the fate of cardiac myocytes.

Differentiation of stem or progenitor cells
into different lineages concerns a series of large-scale transcriptional changes
and chromatin recombination. Tissue-specific transcription factors and
epigenetic modification factors work together to program the epigenome and
establish cell unity, which is further maintained by the epigenetic regulatory
mechanism. In order to initiate cellular programmed design, one special type of
transcription factor, the pioneer transcription factor, inserts
development-silenced genes into the "enclosed" chromatin covered by
nucleus. Pioneer factor alone is not enough to activate genes, but it gives
chromatin the ability to open transcription. Chromatin open is helpful to the
following recruitment of additional transcription factors and other regulatory
proteins, these proteins work together in the a series of steps of lineage explanation
and heart occurrence process to induce the cell type specific gene program
expression, and multiple transcription factors cooperate with each other and are
integrated in the network of regulation, which strictly control the transcription
program ensuring the normal development of the heart.
Isl 1 is a kind of LIM- homologous domain
transcription factor that is transiently expressed in SHF progenitor cells
prior to differentiation and integrating into cardiac tubes. These cells are
added to the artery and vein poles of the cardiac tube to make it continue to
grow and form the complicated morphogenesis model. The deployment and
differentiation of SHF cardiac progenitor cells are the main reason of human
congenital heart malformation in a very great degree, which highlights the
importance of the more comprehensive understanding of the the mechanism of
heart development mediated by SHF. Genetic studies in mice have shown that Isl
1 plays a key role in the development of SHF, which suggests that Isl
1-deficient mouse embryos lack all structures extracted from SHF, including
right ventricle (RV), outflow tract (OFT) and most atria. Because Isl 1 is
necessary for the proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation into
different cardiac lines of SHF CPC. Recent studies found that Isl 1 variants
and deletions are relevant to congenital heart disease. Although Isl 1 plays a
key role in heart development and disease, detailed insights into its molecular
patterns of action are severely deficient.
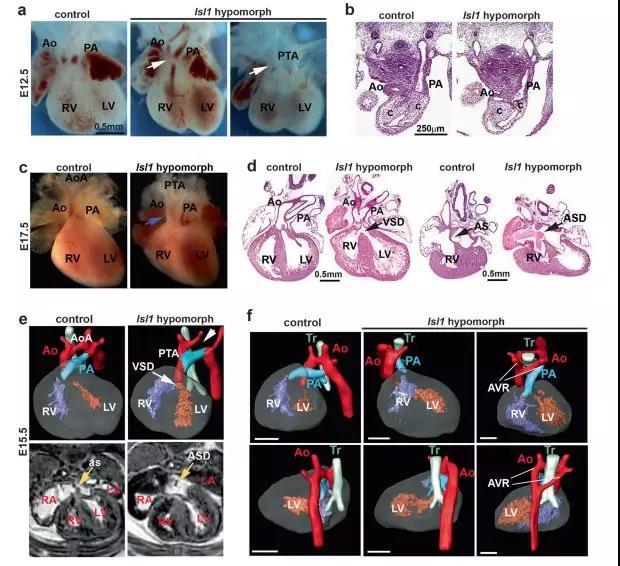
Here, the study shows that Isl1 serves as a
precursor to the myocardial cell lineage through shaping the chromatin
landscape of cardiac progenitor cells. In the Isl1 subtype mouse series showing
congenital heart defects, Isl1 combined genome-wide analysis and RNA- and ATAC-sequencing
of cardiac progenitor cells and their derivatives revealed the downstream
regulatory network of Isl1, which coordinates cardiac initiation. The research
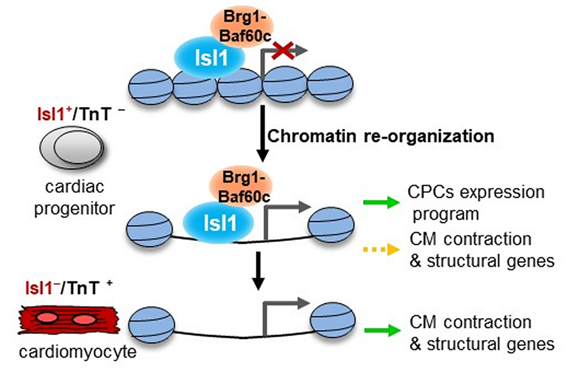
of mechanism shows that Isl1 will combine with condensed chromatin and
cooperate with the SWI/SNF complex based on Brg1-Baf60c so as to promote specific changes of heart
lineage allowed in the chromatin landscape, which contain not only genes that
have key function in cardiac progenitor cells but also highly expressed structure
genes of myocardial cell when Isl1 itself no longer exists. Thus, the Isl1 /
brg1-baf60c complex plays a crucial role in coordinating cardiac genesis and the
epigenetic memory of establishing the fate of cardiac myocardial cells.
Professor Gergana Dobreva from Max Planck Institute
of Cardiopulmonary Research, Prof. Sun Yunfu from TUSM and Prof.Sylvia M. Evans
from University of California, San Diego, are co-corresponding authors of the
paper. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation
of China.
Link:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41422-019-0168-1.pdf
