CD47 is highly expressed in many sorts of tumor cells,
it’s able to send the "don 't eat me" signal to macrophages by
combining SIRP(signal regulatory protein) on them so as to realize the
immune escape for tumor cells[1].The monoclonal
antibody targeting CD47 can enhance the phagocytosis of macrophage to eliminate
tumor cells, while its development remains in the clinical trails stage whose
results revealed that the therapy effect of combination with rituximab is better[2, 3].But the clinical results also showed that CD47
monoclonal antibody has some side effects like the high expression of CD47 in red
blood cells which leads to anemia[4].Thus, looking
for other ways to offset the "don 't eat me" signal seems specifically
important.
Prof. Wang Ping has devoted to studying the tumor
microenvironment for a long time. His research group has online published the study
article titled as Identification of Glutaminyl Cyclase isoenzyme isoQC as
a Regulator of SIRPα-CD47 axis in Cell Research on May 14,
their work through the CRISPR - Cas9 genome-wide screening found that the special
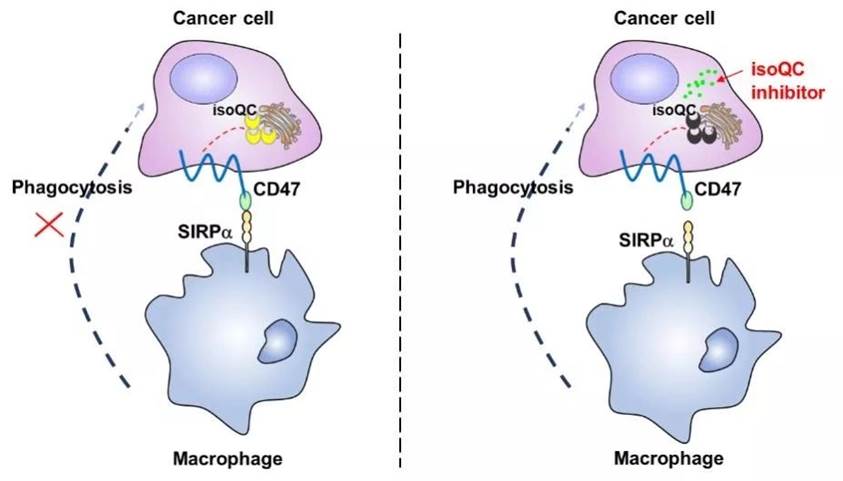
glutamine cyclization modification of N-terminal glutamine residue in CD47 by
isoQC is capable to promote CD47 to combine with SIRP α, and they illustrated new
regulation mechanisms of the CD47-SIRPαpathway in this article.

IsoQC is the glutamine cyclization isozyme positioned in the golgi
apparatus, which can catalyze the glutamine in the N-terminal of substrate
protein into pyroglutamic acid (pGlu) [5, 6].Through
isoQC inhibitors-rescue experiment, this study confirmed that isoQC can regulate
the glutamine cyclization of CD47 with its enzyme activity. By analyzing the
amino acid sequence of CD47 and isoQC substrates, they found that CD47 is the
potential substrates of isoQC and further confirmed that the glutamine
cyclization modification in the N-terminal of CD47 exists by mass spectrometry.
Considering both the experimental results of CC2C6 and B6H12, two different
cloning number antibodies of CD47, and the results of the specific
identification of glutamine cyclization modificated antibody, they concluded
that the Gln in the N-terminal of CD47 can be modified into pGlu by isoQC.
At the same time, this study also proved that isoQC
can regulate the combination of CD47- SIRP through CD47 - SIRPa combining experiments,
and by co-cultivating macrophage cells and tumor cells, isoQC can prevent tumor
cells from the phagocytosis of macrophages. In addition, TCGA data verified
that corresponding patients’ life cycle was significantly cut down as the
expression of isoQC increase in various tumors. All these statistics suggest
that isoQC could be used as a potential drug target clinically.
In summary, the work found that isoQC is an important
regulation factor in the CD47–SIRPαpathway by whole genome screening and it could
be used as a potential drug target in tumor immunotherapy.
It is reported that Wu Zhiqiang, Weng Linjun and Zhang
Tengbo from Prof. Wang Ping’s research group are co-first author of this
article, and Prof. Wang Ping is the corresponding author.
It’s notable that this study revealed similar mechanism
with the work of Prof. Ton N. Schumacher from Amsterdam Cancer Institute
in the Netherlands, whose article titled as Glutaminyl cyclase is an
enzymatic modifier of the CD47- SIRPα axis and a target for cancer
immunotherapy was published in Nature Medicine in March, 2019.

Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41422-019-0177-0
Reference:
1. Barclay, A.N. & Van den Berg, T.K. The
interaction between signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) and CD47:
structure, function, and therapeutic target. Annu Rev Immunol 32, 25-50 (2014).
2. Li, Y. CD47 Blockade and Rituximab in Non-Hodgkin's
Lymphoma. N Engl J Med 380, 497 (2019).
3.Chao, M.P. et al. Anti-CD47 antibody synergizes with
rituximab to promote phagocytosis and eradicate non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cell 142,
699-713 (2010).
4.Oldenborg, P.A. et al. Role of CD47 as a marker of
self on red blood cells. Science 288, 2051-2054 (2000).
5. Cynis, H. et al. Isolation of an isoenzyme of human
glutaminyl cyclase: retention in the Golgi complex suggests involvement in the
protein maturation machinery. J Mol Biol 379, 966-980 (2008).
6. Cynis, H. et al. The isoenzyme of glutaminyl
cyclase is an important regulator of monocyte infiltration under inflammatory
conditions. EMBO Mol Med 3, 545-558 (2011).
